Windows 10 and Windows 11 both allow users to run Linux inside Windows officially via the Windows subsystem for Linux. There are certain limitations to it, though. Your distro choices are limited to Ubuntu, SUSE Linux Enterprise, and OpenSUSE Leap. You’re also limited to the command line. So, there are still many reasons to create a Linux virtual machine on Windows. It’s also pretty easy to run a Linux VM on Windows.
Especially if you’re thinking about dual-booting or installing a Linux distro on your PC, trying out a Linux virtual machine is a good idea. There are a few software choices when it comes to running a Linux VM on Windows or any virtual machine. Most people prefer Virtual Box because it’s free and open source.
Requirements for Linux Virtual Machine on Windows
For this tutorial, that is what we will be using. As for the Linux distro, you can create a Linux virtual machine with any distro of your choice. That choice does not affect the method of creating or running the virtual machine. Still, since Ubuntu is a popular choice, we will be creating a Virtual Box Ubuntu VM for this tutorial.
Download: Virtual Box (EXE), Ubuntu (ISO)
Create Virtual Box Ubuntu Virtual Machine
With Virtual Box installed and your Linux distro’s installable ISO image downloaded, we can start creating a Linux virtual machine.
- Open Virtual Box.
- Click on New.
- Name your Virtual Machine and select the downloaded ISO file.
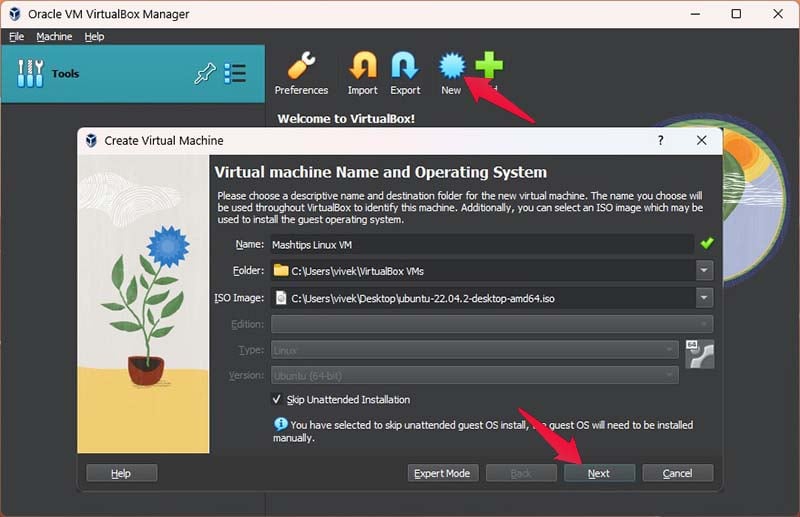
- Make sure you do not check Skip Unattended Installation.
- Click Next.
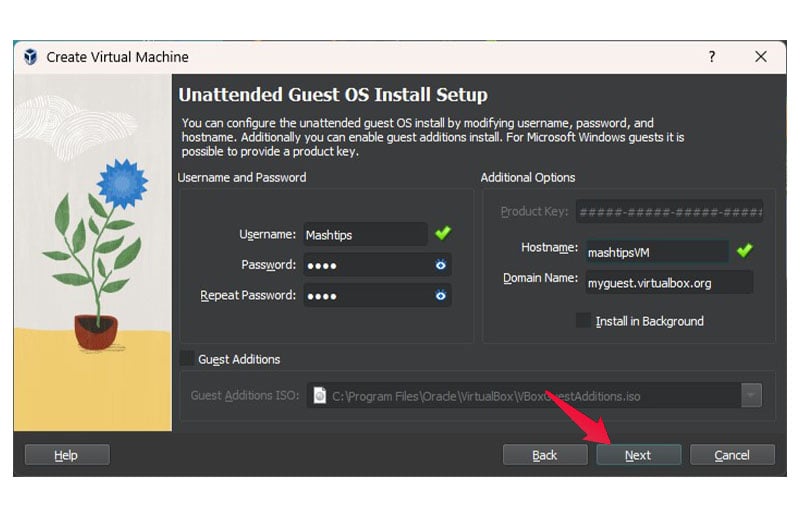
- Set the Username and Password for your OS. By default, the username is vboxuser and the password is changeme.
- Set a hostname for your Linux virtual machine.
- Click Next.
- Use the sliders to adjust the amount of RAM and processing cores you wish to grant your Linux VM. Depending on your system hardware, Virtual Box marks the sliders in green, orange and red, meaning safe, maybe safe, and unsafe.
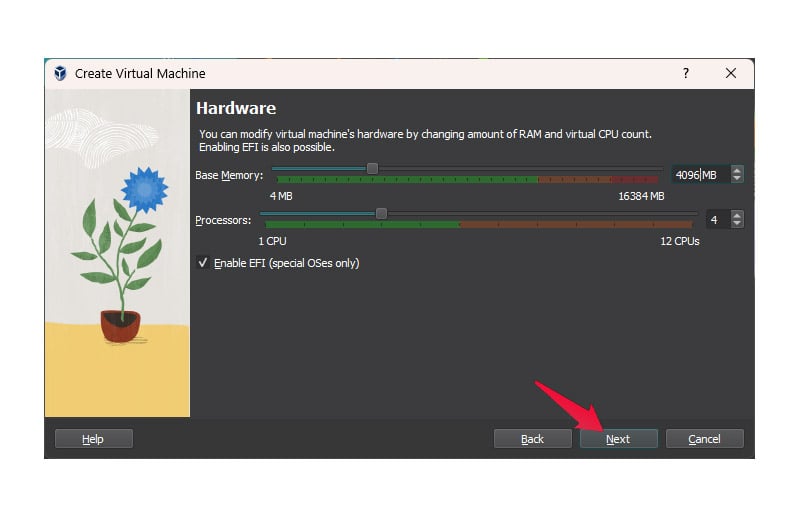
- Linux is not resource intensive, so 4 GB of RAM and a couple of CPUs are fine to run a Linux VM. Click Next when ready.
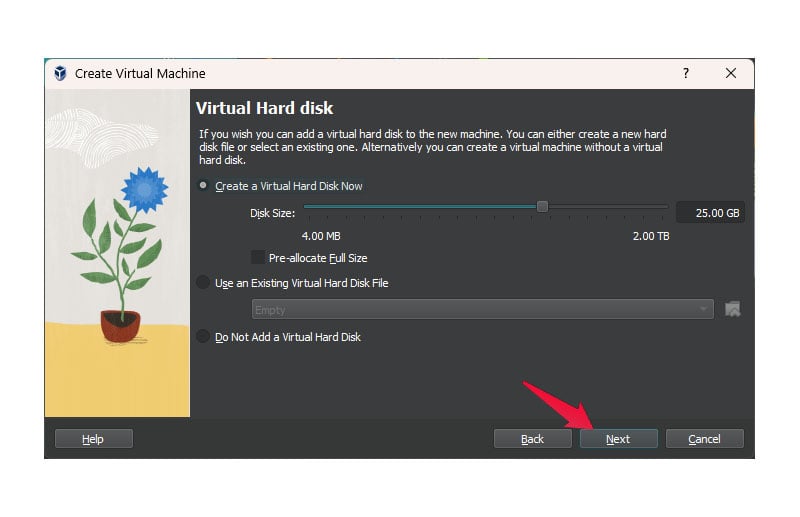
- Set the Disk size slider as per your preference. If you only want to try out a Linux distro, 15 GB to 20 GB is enough space.
- Click Next.
- Click Finish and Virtual Box will do the rest.
Run VirtualBox Ubuntu VM
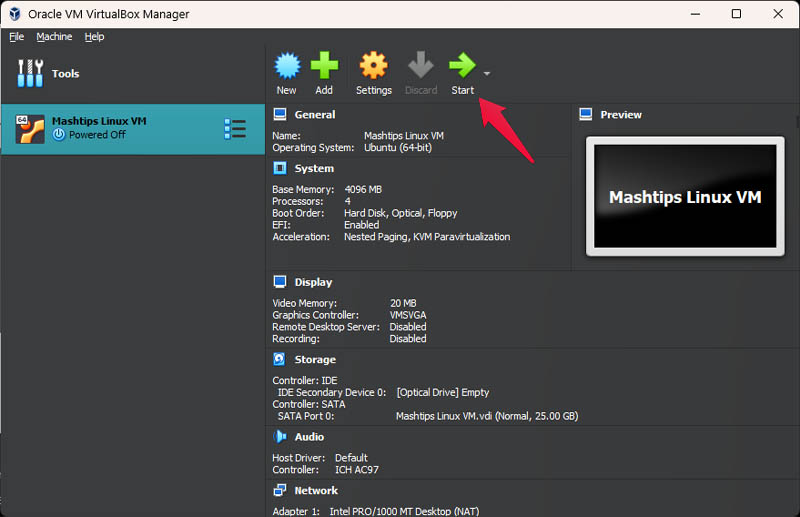
Your Linux virtual machine is ready to run. To start it, click the Start button in Virtual Box. You will see Show instead of Start if the machine is already running. You may see an error when running the machine for the first time. All you have to do is select the downloaded ISO file again and click Mount and Retry Boot.
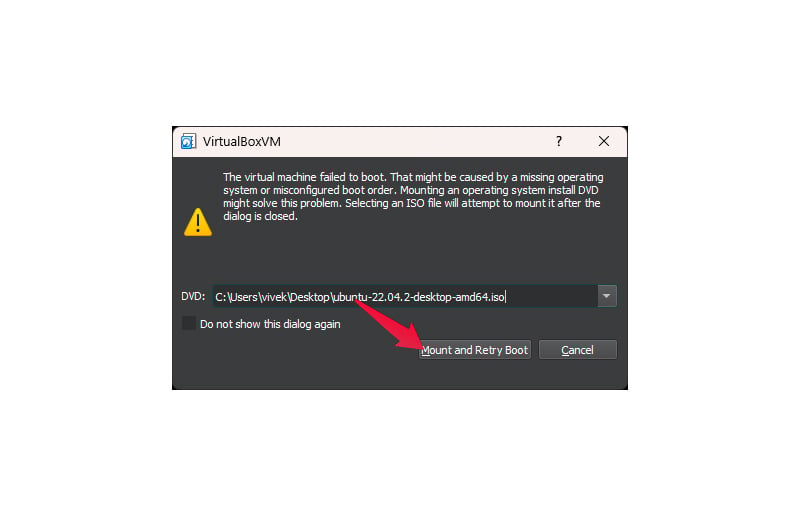
Your ISO file boot up the same way it does from a CD or a bootable drive. So, you will be greeted by the installer for Ubuntu or the Linux distro you used.
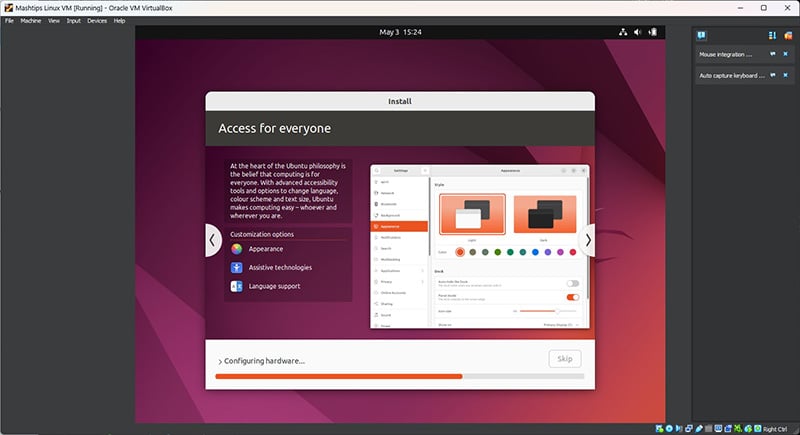
You can see Ubuntu being installed on the VM we just created.
Install Virtual Box Extensions
If you’ve created a Linux virtual machine and plan to use it for various things, you might want to look at virtual box extensions. Virtual Box extensions add support for USB drives, webcams, other external peripherals, and more. You can download the VirtualBox 7.0.8 Oracle VM VirtualBox Extension Pack from the Virtual Box download page. Once downloaded, follow the steps below to install the virtual box extensions pack.
- Open Virtual Box.
- Click on File.
- Go to Tools > Extension Pack Manager.
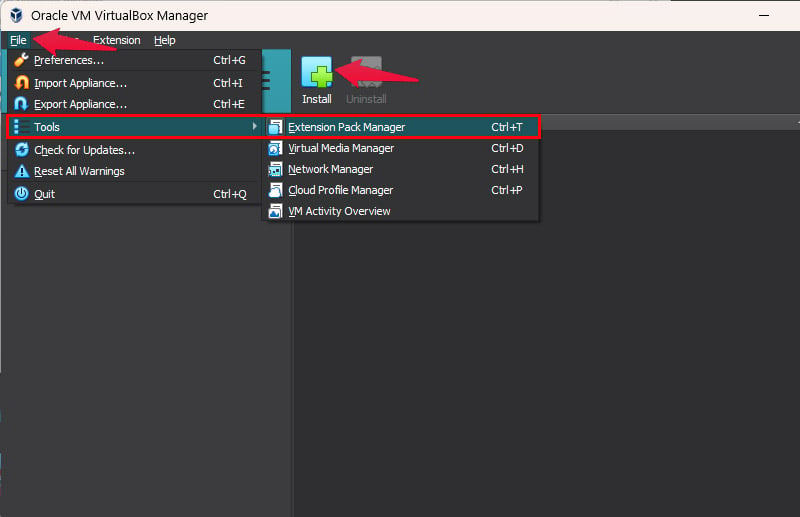
- Click Install.
- Select the downloaded extensions pack.
- Click Install.
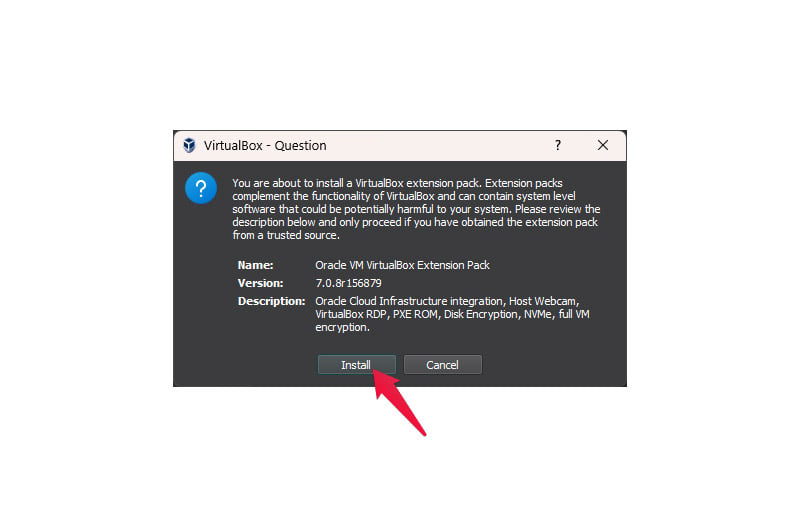
- Click I agree.
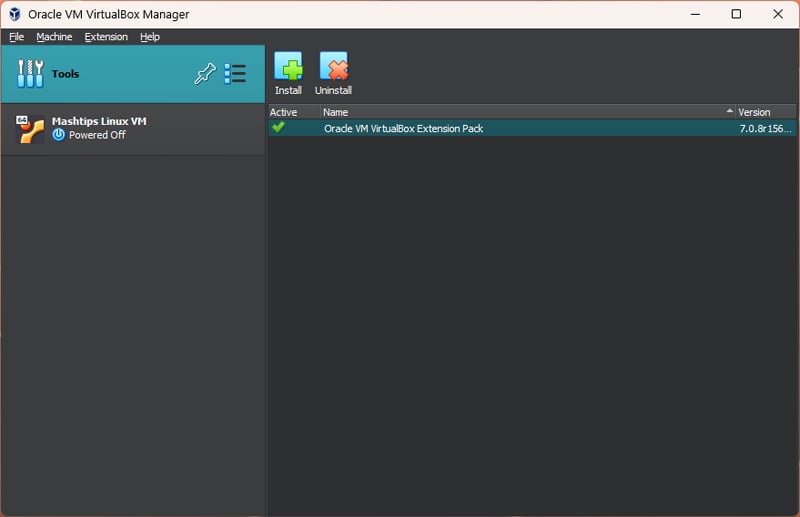
Once installed, You will see the extension pack in the Extensions Pack Manager.
Windows 10 and 11 offer other ways to run a Linux Virtual Machine using Hyper-V. However, Hyper-V is a Windows feature reserved for Windows Pro and Enterprise editions. With Virtual Box, you can run a Linux VM on any Windows PC, even those running Windows Home edition, which most users have.

This is a great post! I have been wanting to learn more about Linux so this is perfect for me.