Even as Android keeps getting more and more locked down each year, it is still much more open than many other options out there. One of the things it makes possible is the ability to unlock the bootloader. The bootloader is locked by default for security reasons but can be unlocked easily. There is the OEM lock, which prevents anyone from unlocking the bootloader. If you want to unlock the bootloader, you’ll first have to enable OEM unlock.
Here we will see what is OEM unlock and how to unlock the bootloader with OEM unlock on your Android phone.
Enable OEM Unlock on Android
Normally, unlocking the bootloader on an Android device is as easy as a single fast boot command. But this means anyone with physical access to your device can connect it to a computer and simply unlock the bootloader with a command. Since all of this happens outside the OS, they wouldn’t need to unlock your device using your PIN or password. It’s clearly not a very secure situation. Therefore, manufacturers put in place an OEM lock.
Related: How to Get Google Camera Night Sight Mode on Any Android
Usually, you’ll have the option to enable OEM Unlock under the hidden Developer settings. Depending on the manufacturer of your device though, the route to that option could differ. Here we have covered the steps that will be valid for most Android devices especially those running a close-to-stock Android build, such as OnePlus, Google, Sony, etc.
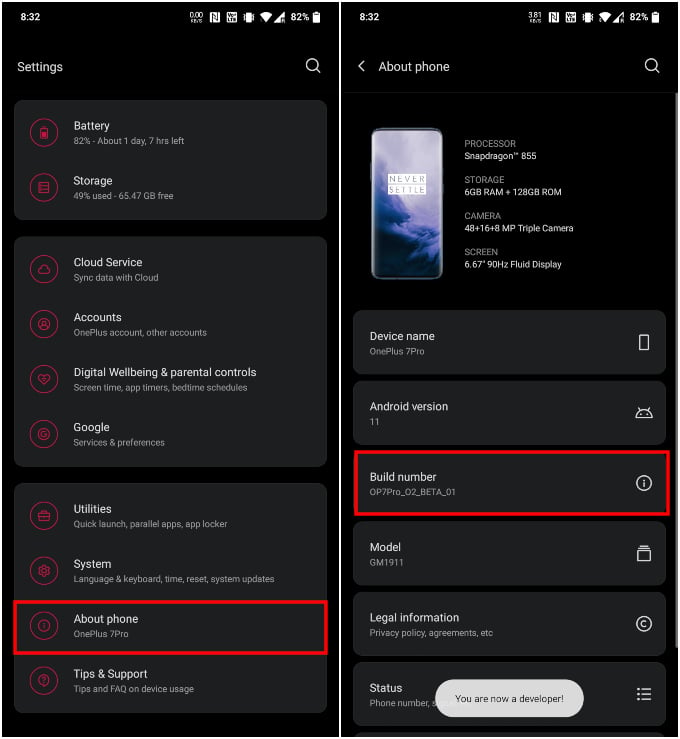
- Open the Settings app.
- Scroll down to About phone.
- Tap on the Build number entry 7 times repeatedly and enter your PIN when asked.
- You should see a toast message saying “You are now a developer!”
- Go back to Settings and select System.
- Tap on Developer options here. On some devices, you may have to tap Advanced to see Developer options.
- Turn on the toggle next to OEM unlocking.
- Enter your PIN again, if asked.
- Select Enable on the confirmation popup.
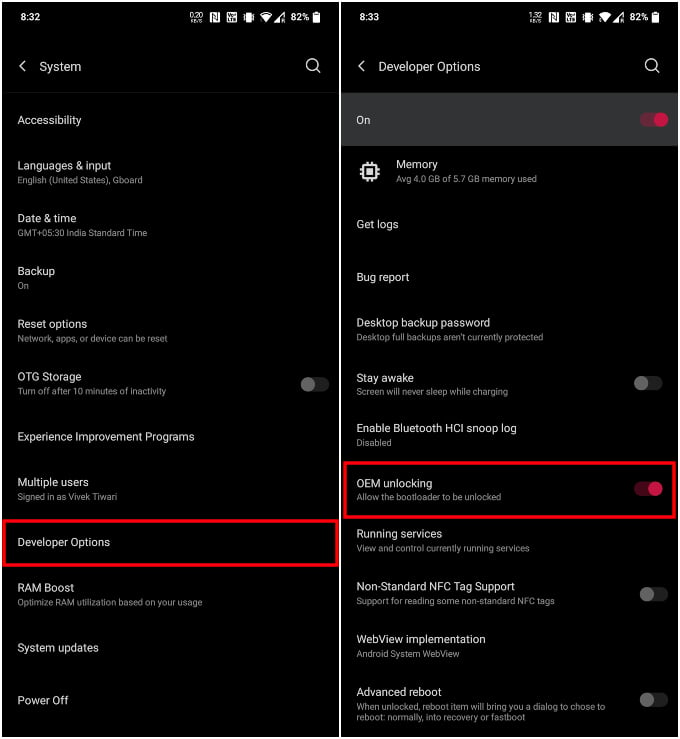
And that should do it. Yes, it’s simply a toggle hidden under developer options. But this little toggle makes sure that anyone with physical access to your device cannot simply unlock the bootloader. They’ll have to bypass your lock screen, and enter your PIN to even enable developer options and enable OEM unlock. Naturally, it’s not a wise idea to keep OEM unlocking enabled if you don’t really need to.
Related: How to Install Android Apps on Amazon Kindle Fire (No Rooting)
Is OEM Unlock Same as Root
These are some technical waters that we’re navigating here. So, if you’re not familiar with the terms, OEM unlock is not the same as root. Rooting is a separate and different process that can only take place, normally, after OEM unlock has been enabled.
OEM Unlock simply gives you the ability to unlock the bootloader. While rooting is a process that gives you complete access to your device’s OS, including the ability to break things. Once you unlock the bootloader, only then can you go ahead and root your device.
What Does Unlocking the Bootloader Do
The bootloader is simply a piece of code that is responsible for the booting process. It is what brings up the kernel on top of which the OS then boots up. A locked bootloader is one that will only boot up a specific Operating System, such as the boot image installed by the manufacturer.
Unlocking the bootloader allows you to boot up any custom Android image that is bootable. This opens the doors to custom recoveries, custom ROMs, and even custom kernels. These are created mostly by third-parties, and the manufacturer does not take any responsibility for them.
Related: How to Fix Grub Bootloader after Deleting Ubuntu Partition
Is OEM Unlock Safe
You may also wonder if OEM unlock is even safe to do. The answer to that will depend on what you mean by safe. In isolation, OEM unlock is safer than installing an app on your phone from the Google Play Store. However, most of the risks associated OEM unlock are not part of the process of unlocking itself. So, as far as the process to enable OEM unlock goes, it’s pretty safe. Your device will still work as intended. Enabling OEM unlocking does not even void your warranty by itself.
The real risks associated with OEM Unlock are actually what happens after the fact.
An unlocked device is prone to being hacked by anyone with a computer and the know-how. They could unlock the bootloader and install any image they want and use your device as they want. It will certainly be difficult without your PIN or password but not impossible. Fortunately, Android has many security layers built to prevent anyone from getting access to your data. In most cases, your data will be completely wiped during such attempts.
Related: Give Your Android Smartphone a Google Pixel Theme Makeover
Another point of potential risk comes from you, the user. OEM unlock is merely a barrier to a certain goal since it doesn’t do much by itself. So, if you’ve gone through the OEM unlock process, you probably had other things in mind. Installing a custom ROM, kernel, recovery, and even rooting are all processes that come with a significant amount of risk. With the OEM lock removed, the device is open to the risks posed by the user, who may or may not fully understand what they’re doing.

How can one remove a device from being Blacklisted